夏乙 郭一璞 发自 凹非寺
量子位 出品 | 公众号 QbitAI
什么!未连接到互联网!!
明明是联网状态,为什么我想访问的页面
无!法!打!开!
淡定。
作为一个Google 遗传算法,让一个AI系统独秀于浏览器之中。
我们把精华的部分截取了一下,就是下面这段视频。
动图版:
速度已经快到飞起
总而言之,一句话,这个AI能轻松玩到2万多分……
你能玩到几分?大概率是玩不到这个成绩的吧。毕竟在chromedino.com页面上,人类玩家的历史最高分是18842。
不过,上传这段视频的作者,并没有详细公布他用的方法,当然也没有给出一个开源的地址。不过不要紧,也有别人公开分享了更多细节。
例如,GitHub上就有一个开源的代码“IAMDinosaur”,同样也是利用神经网络 遗传算法,来搞定恐龙跳一跳。
地址在此:https://github.com/ivanseidel/IAMDinosaur
美中不足,上面这个项目也没有配上太详尽的解读。然而好消息是,最近有个国外的小哥Ravi Munde,列了一份非常详尽的教程。
这个教程用的方法是强化学习中的Q-learning,比较适合入门练手,而且对硬件的要求不高。
量子位搬运这份教程如下。
Q-learning了解/复习一下
对动物来说,强化学习的能力是与生俱来的。拿儿童学步来举例,如果小朋友努力的迈出第一步,就会获得父母的鼓励——可能是鼓掌叫好,也可能是一块糖;但如果小朋友坚决不肯学习走路,那父母就不会给它糖吃了。强化学习就是依照这类激励行为而设置的。
而在这个游戏中,对我们的AI小恐龙来说,强化学习需要让他在无监督的情况下,先认识到做出不同动作的结果,并且以获得高分为最高激励。
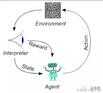
一个典型的强化学习闭环
Ravi Munde用Q-learning模拟了一个特殊函数,这个函数驱动AI在不同状况下做出正确的选择。
Q-learning是强化学习的一种无模型实现,根据Q值对每个状态进行判断此时如果采取行动,能获得怎样的奖励。一个样本Q表让我们了解数据的结构。在恐龙跑酷游戏中,状态是当前的游戏截图,能采取的行动是跳或不跳[0,1]

一个样本Q表
Ravi Munde决定用深度神经网络来决定小恐龙何时起跳,而且要在最简单的强化学习实现基础上,引入不同参数来辅助它。
缺乏已标记的数据让强化学习非常不稳定。为了获得适用于这个游戏的数据,Munde小哥决定,先让小恐龙自己瞎跳几千次,把每个动作的反馈记下来,然后从数据中随机挑选一些来训练模型。
但之后,Munde小哥发现,他训练了一个倔强的模型——模型坚定的认为,跳,一定比不跳好。所以,为了让模型在训练时能在跳与不跳之间多尝试一下,他引入了一个函数ɛ来决定行动的随机性,然后再逐渐减小它的值来削减随机性,最终让模型去选择最有可能获得奖励的行动。
赞誉分布(Credit Assignment)问题可能会让模型陷入混乱——目前获得的奖励究竟来自于过去的哪个行为呢?在恐龙跑酷游戏中,小恐龙跳到半空中后无法再次跳跃,但模型可能会在恐龙处于半空中时发出跳跃指令,这种情况就让恐龙非常容易砸到仙人掌上。
在这种情况下,“砸到仙人掌上”这个负反馈实际上是此前上一次做出跳跃决定的结果,而不是刚刚恐龙在半空中时做出的跳跃结果所导致的。
在面临这种问题的情况下,可以引入贴现因子(Discount Factor)γ来决定模型做出动作时看得多远。γ间接解决了赞誉分布问题,在这个游戏中,当γ=0.99时,模型认识到在无障碍时随便跳会导致真的遇到障碍时自己正在半空中,无法继续跳跃。
除了这两个参数之外,后面就几乎不需要任何参数了。
#game parametersGAMMA = 0.99 # decay rate of past observations original 0.99OBSERVATION = 50000. # timesteps to observe before trainingEXPLORE = 100000 # frames over which to anneal epsilonFINAL_EPSILON = 0.0001 # final value of epsilonINITIAL_EPSILON = 0.1 # starting value of epsilonREPLAY_MEMORY = 50000 # number of previous transitions to rememberBATCH = 32 # size of minibatchFRAME_PER_ACTION = 1
你需要准备的是
Python 3.6
Selenium
OpenCV
PIL
Chromium driver for Selenium
Keras
略微解释一下这几个工具。
构建这个AI模型,需要用Python编程。而游戏是用JavaScript写成的。所以,得借助一些工具才能更好地沟通。
Selenium是一种流行的浏览器自动化工具,用于向浏览器发送操作指令,以及获取各种游戏参数。
接口的事情搞定了,还得想办法获得游戏截屏。用Selenium也行,但是速度很慢,截屏和处理一次大约得1秒钟。
用PIL和OpenCV能够更好地完成截屏和图像预处理,可以达到5fps的帧率。你可能觉得还是慢,但已经足够对付这个游戏了。
游戏模块
下面这个模块,实现了Python和浏览器(使用Selenium)的沟通。
'''* Game class: Selenium interfacing between the python and browser* __init__(): Launch the broswer window using the attributes in chrome_options* get_crashed() : return true if the agent as crashed on an obstacles. Gets javascript variable from game decribing the state* get_playing(): true if game in progress, false is crashed or paused* restart() : sends a signal to browser-javascript to restart the game* press_up(): sends a single to press up get to the browser* get_score(): gets current game score from javascript variables.* pause(): pause the game* resume(): resume a paused game if not crashed* end(): close the browser and end the game'''class Game: def __init__(self,custom_config=True): chrome_options = Options() chrome_options.add_argument("disable-infobars") self._driver = webdriver.Chrome(executable_path = chrome_driver_path,chrome_options=chrome_options) self._driver.set_window_position(x=-10,y=0) self._driver.set_window_size(200, 300) self._driver.get(os.path.abspath(TensorFlow后端的Keras来搭建的模型:
#model hyper parametersLEARNING_RATE = 1e-4img_rows , img_cols = 40,20img_channels = 4 #We stack 4 framesACTIONS = 2def buildmodel(): print("Now we build the model") model = Sequential() model.add(Conv2D(32, (8, 8), strides=(4, 4), padding='same',input_shape=(img_cols,img_rows,img_channels))) #20*40*4 model.add(Activation('relu')) model.add(Conv2D(64, (4, 4), strides=(2, 2), padding='same')) model.add(Activation('relu')) model.add(Conv2D(64, (3, 3), strides=(1, 1), padding='same')) model.add(Activation('relu')) model.add(Flatten()) model.add(Dense(512)) model.add(Activation('relu')) model.add(Dense(ACTIONS)) adam = Adam(lr=LEARNING_RATE) model.compile(loss='mse',optimizer=adam) print("We finish building the model") return model
开始训练
接下来,就是见证奇迹的时刻~~
也就是用一段代码来训练模型,这段代码的任务是:
从无操作开始,得到初始状态initial state(s_t)
观察玩游戏的过程,代码中的OBSERVATION表示步数
预测一个操作的效果
在Replay Memory中存储经验
训练阶段,从Replay Memory里随机选择一组,用它来训练模型
如果game over了,就重开一局
更详细的,可以看这段自带注释的代码:
'''Parameters:* model => Keras Model to be trained* game_state => Game State module with access to game environment and dino* observe => flag to indicate wherther the model is to be trained(weight updates), else just play'''def trainNetwork(model,game_state): # store the previous observations in replay memory D = deque() #load from file system # get the first state by doing nothing do_nothing = np.zeros(ACTIONS) do_nothing[0] =1 #0 => do nothing, #1=> jump x_t, r_0, terminal = game_state.get_state(do_nothing) # get next step after performing the action s_t = np.stack((x_t, x_t, x_t, x_t), axis=2).reshape(1,20,40,4) # stack 4 images to create placeholder input reshaped 1*20*40*4 OBSERVE = OBSERVATION epsilon = INITIAL_EPSILON t = 0 while (True): #endless running loss = 0 Q_sa = 0 action_index = 0 r_t = 0 #reward at t a_t = np.zeros([ACTIONS]) # action at t #choose an action epsilon greedy if random.random() <= epsilon: #randomly explore an action print("----------Random Action----------") action_index = random.randrange(ACTIONS) a_t[action_index] = 1 else: # predict the output q = model.predict(s_t) #input a stack of 4 images, get the prediction max_Q = np.argmax(q) # chosing index with maximum q value action_index = max_Q a_t[action_index] = 1 # o=> do nothing, 1=> jump #We reduced the epsilon (exploration parameter) gradually if epsilon > FINAL_EPSILON and t > OBSERVE: epsilon -= (INITIAL_EPSILON - FINAL_EPSILON) / EXPLORE #run the selected action and observed next state and reward x_t1, r_t, terminal = game_state.get_state(a_t) last_time = time.time() x_t1 = x_t1.reshape(1, x_t1.shape[0], x_t1.shape[1], 1) #1x20x40x1 s_t1 = np.append(x_t1, s_t[:, :, :, :3], axis=3) # append the new image to input stack and remove the first one # store the transition in D D.append((s_t, action_index, r_t, s_t1, terminal)) D.popleft() if len(D) > REPLAY_MEMORY #only train if done observing; sample a minibatch to train on trainBatch(random.sample(D, BATCH)) if t > OBSERVE s_t = s_t1 t = t 1 print("TIMESTEP", t, "/ EPSILON", epsilon, "/ ACTION", action_index, "/ REWARD", r_t,"/ Q_MAX " , np.max(Q_sa), "/ Loss ", loss)
将这个模型用到从Replay Memory里随机选择的一批上:
def trainBatch(minibatch):for i in range(0, len(minibatch)): loss = 0 inputs = np.zeros((BATCH, s_t.shape[1], s_t.shape[2], s_t.shape[3])) #32, 20, 40, 4 targets = np.zeros((inputs.shape[0], ACTIONS)) #32, 2 state_t = minibatch[i][0] # 4D stack of images action_t = minibatch[i][1] #This is action index reward_t = minibatch[i][2] #reward at state_t due to action_t state_t1 = minibatch[i][3] #next state terminal = minibatch[i][4] #wheather the agent died or survided due the action inputs[i:i 1] = state_t targets[i] = model.predict(state_t) # predicted q values Q_sa = model.predict(state_t1) #predict q values for next step if terminal: targets[i, action_t] = reward_t # if terminated, only equals reward else: targets[i, action_t] = reward_t GAMMA * np.max(Q_sa) loss = model.train_on_batch(inputs, targets)
主体方法
调用下面的方法,就能启动上面的训练流程:
#argument: observe, only plays if true, else trainsdef playGame(observe=False): game = Game() dino = DinoAgent(game) game_state = Game_sate(dino,game) model = buildmodel() trainNetwork(model,game_state)
结果
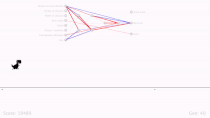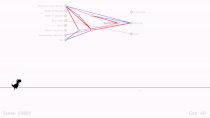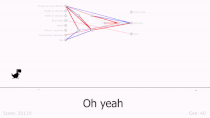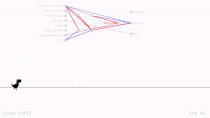
这个模型,小哥用一周的时间训练了200万帧,其中前100万帧用来调整游戏参数修补bug,后100万帧真正用来训练。
现在,这个模型的最好成绩是265分。从下面的得分和损失变化图里,能看出模型的loss在后100万帧逐渐稳定,比较低,但是会随时间波动。

游戏得分

后100帧的损失(loss)
目前的局限
虽然这个模型后来表现还算可以了,但比人类还是差了一大截。
当然,别忘了这个小哥比较穷,他只有一个i7的CPU。
他认为,模型学得还不够快,得分还不够高,要怪这样几个因素:一是因为用CPU来学习,它总是掉帧;二是供这个AI来玩耍的图像实在是太小了,只有40×20,在当前的模型架构下就可能导致了特征的损失,还拖慢了学习速度。
如果改用GPU,说不定……
相关链接
用GPU究竟会不会改善,你们可以拿这份代码来试试:
https://github.com/ravi72munde/Chrome-Dino-Reinforcement-Learning
原文地址:
https://medium.com/acing-ai/how-i-build-an-ai-to-play-dino-run-e37f37bdf153
One More Thing
其实嘛,让AI搞定小恐龙这件事,本质上跟让AI搞定Flappy Bird是一样的。如果你想深入研究一下这件事,这里再推荐两篇。
机器学习玩转Flappy Bird全书:六大“流派”从原理到代码
使用神经网络 遗传算法玩转Flappy Bird | 教程
就酱~
— 完 —
诚挚招聘
量子位正在招募编辑/记者,工作地点在北京中关村。期待有才气、有热情的同学加入我们!相关细节,请在量子位公众号(QbitAI)对话界面,回复“招聘”两个字。
量子位 QbitAI · 头条号签约作者
վ'ᴗ' ի 追踪AI技术和产品新动态